Prostate cancer is in fourth place among tumors in men, and after 60 years it takes second place and is a serious health problem.
What you need to know about the structure of the prostate gland?
The prostate gland is a small organ that covers the initial section of the urethra (urethra) at the exit from the bladder, tightly attached to the rectum. Its main function is to secrete secretions that thin the sperm and contain vitamins, proteins, enzymes and other essential nutrients for sperm.
What you need to know about prostate cancer?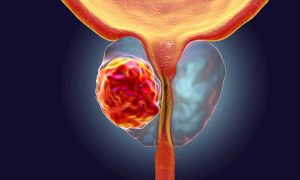
Prostate cancer is a malignant tumor that develops mainly in the peripheral parts of the gland and is usually characterized by slow growth. However, if the tumor develops slowly, therefore, there are no manifestations in the early stages and the patient is unaware of the presence of the disease. Long-term absence of treatment will lead to a further increase in the tumor, spread to nearby organs and transfer of tumor cells with blood to other organs: bones, lungs, liver. Considering the structure of the prostate gland, in the later stages it is possible to grow into the bladder, rectum and pelvic walls. Unfortunately, it is often in the later stages that men go to the doctor for the first time.
What are the causes of prostate cancer?
The reasons are not fully understood, but there are predisposing factors:
Age. There is a clear relationship with age: starting at the age of 45, the risk of developing cancer increases. The older the man, the higher the likelihood of a prostate tumor.
Genetic reasons. If a family history of cancer is known in blood relatives in the male line (grandfather, father, uncle, brother), there may be changes in the genes (mutations in the BRCA1 / BRCA2 genes)
Hormone imbalance
Obesity
Smoking
Alcohol abuse
Frequent change of sex partners and STIs
What are the manifestations of prostate cancer?
Conventionally, the signs of cancer can be divided into early and late.
Early signs are associated with enlargement of one or both lobes of the prostate gland. As the prostate covers the urethra, urinary complaints occur:
Frequent painless urination, including night trips to the toilet
Paradoxical urinary retention: with strong urge, the urine stream is sluggish or absent
Feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder
Erectile dysfunction and potency
Pain during intercourse
Sometimes there is blood in the urine
These symptoms can occur one at a time or in combination and can be a sign of other diseases of the genitourinary tract, therefore, when they appear, you need to consult a urologist.
Lack of complaints and / or untimely access to a doctor leads to the emergence of “late symptoms” of prostate cancer:
Lower abdominal pain shooting in the rectum
Pain in the spine, pelvic bones, ribs (evidence of bone metastases)
Acute urinary retention (when the swelling has enlarged enough to obstruct the lumen of the urethra)
Decreased appetite, weakness, weight loss (exposure to tumor toxins)
How to prevent the development of cancer?
Regularly examined by a urologist, regardless of the presence or absence of complaints
Undergo an annual digital examination of the prostate gland and transrectal ultrasound as directed by a doctor.
For men over 45 years old, donate blood for total PSA, percentage of free PSA and PHI (prostate health index).
PSA (prostate-specific antigen) can increase with benign changes in the prostate gland (adenoma), therefore, with a single increase, the doctor will prescribe a second study. Prostate Health Index – Usually prescribed when PSA levels are between 2 and 10 ng / ml.
The most accurate analysis that allows you to diagnose a tumor is a histological examination. For it, a biopsy is performed – 12 pieces of prostate https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Prostate tissue are taken, and this is a rather painful and traumatic procedure.
PSA and PHI (Prostate Health Index) tests are taken as normal blood tests from a vein. Their main purpose is to identify patients in need of biopsy.